Eared Dove
The Eared Dove (Zenaida auriculata), Read in Spanish
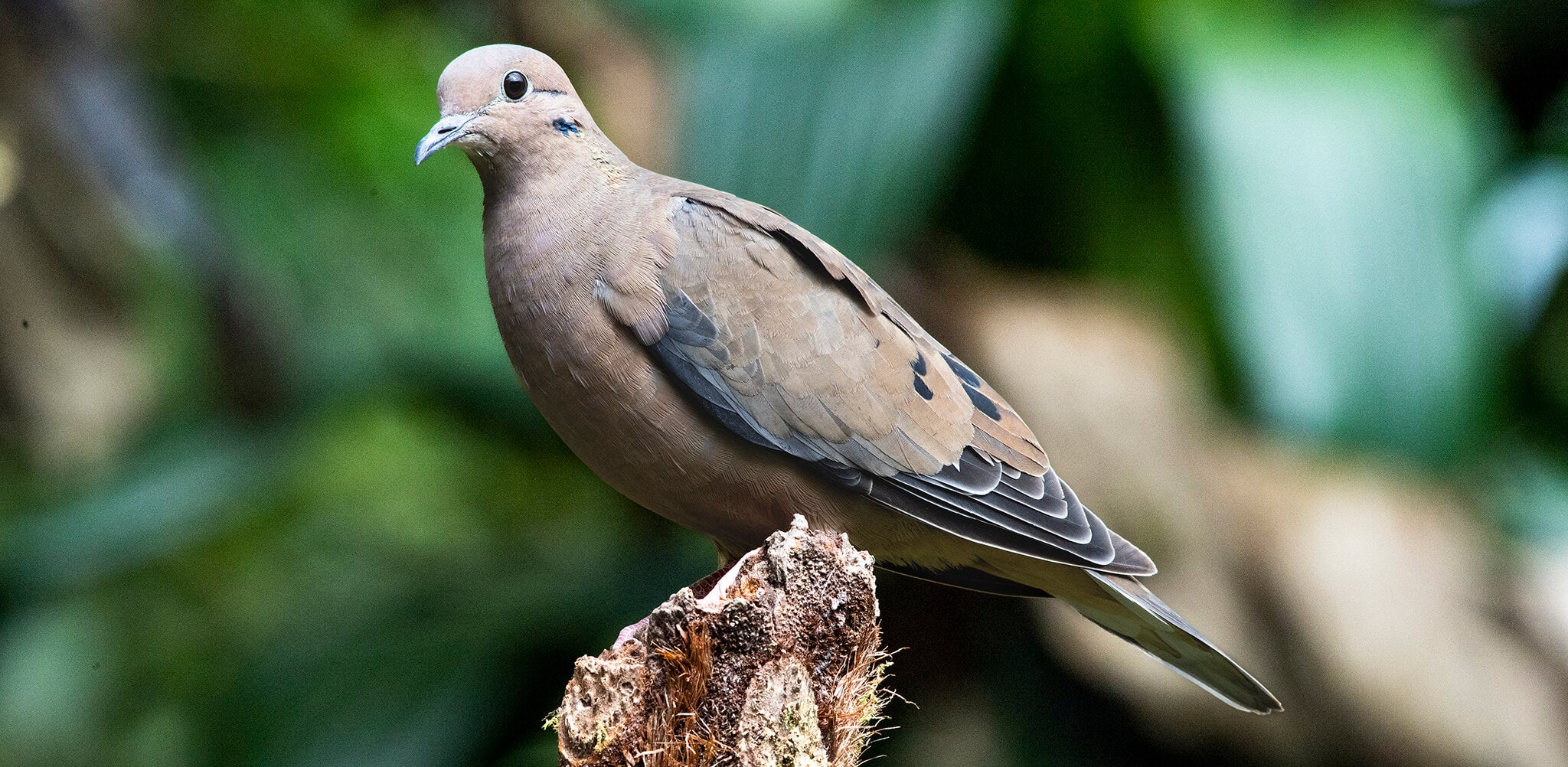
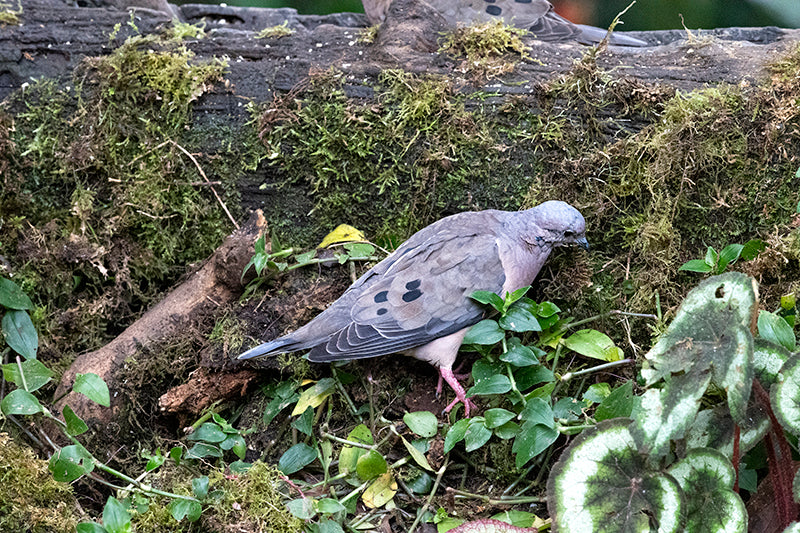
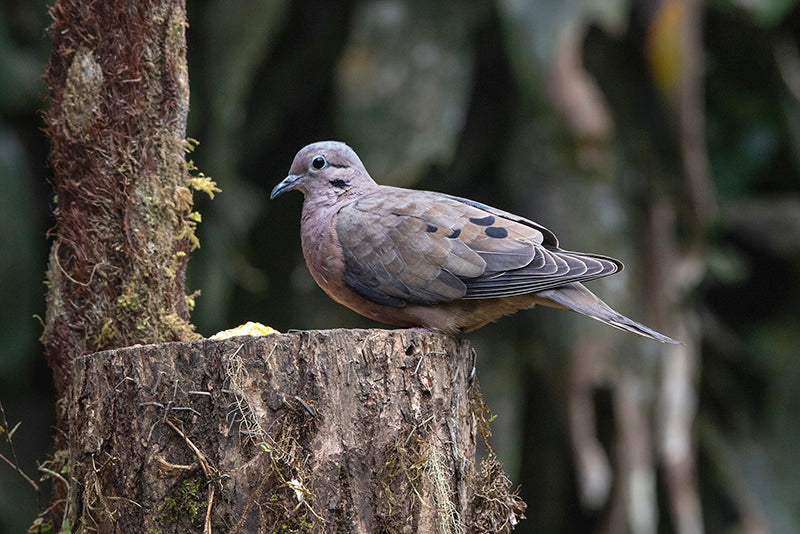
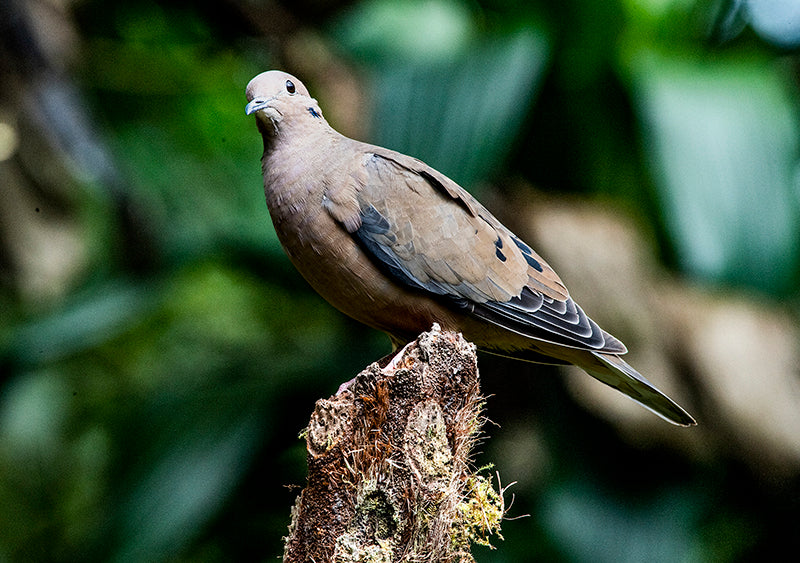
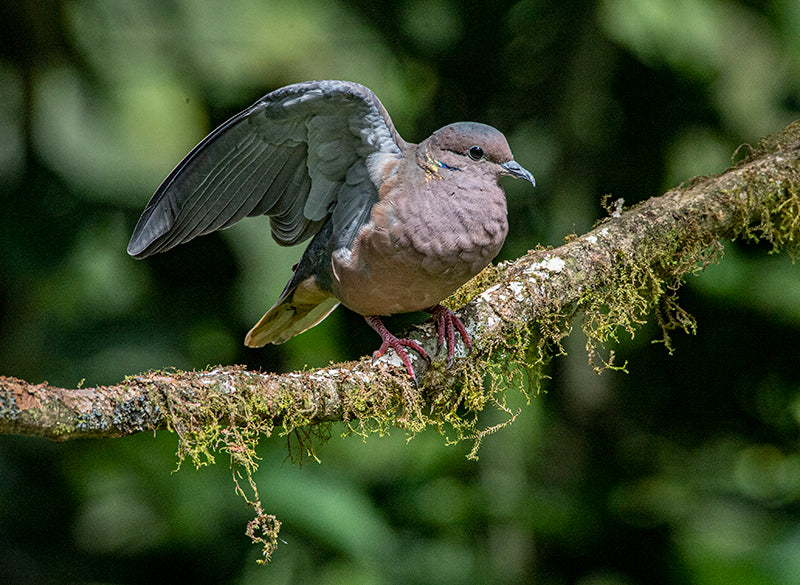
Appearance: The Eared Dove is a medium-sized bird with a distinctive appearance. It has a grayish-brown body, pinkish underparts, a noticeable black collar on the nape of the neck, and prominent black spots on its wings. One of its most defining features is the eartuft or "ear" patch behind its eyes, which gives it its name.
Habitat: The Eared Dove is a versatile species that can be found in a wide range of habitats across Colombia. It is commonly seen in open woodlands, forest edges, farmlands, parks, gardens, and urban areas. This adaptable bird can thrive in both rural and urban environments.
Behavior: Eared Doves are typically gregarious birds, often seen in small to large flocks foraging for seeds, grains, and fruits on the ground. They are known for their rapid and direct flight, often with a characteristic whistling sound produced by their wings.
Breeding: Eared Doves breed throughout the year, with a peak in the breeding season during Colombia's rainy seasons when food availability is high. They construct flimsy nests made of twigs and grasses in trees or shrubs. Females usually lay 1-2 eggs, and both parents share the responsibility of incubating the eggs and raising the young.
Conservation Status: The Eared Dove is widespread and considered a species of Least Concern globally by the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN).
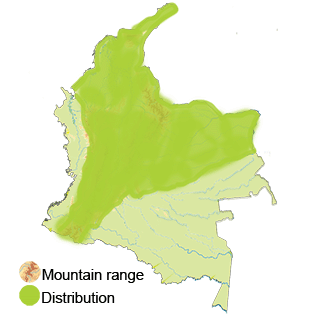
Distribution
The Eared Dove (Zenaida auriculata)
Andean Region: The Eared Dove is commonly found in the Andean region of Colombia. This region includes the Andean mountain range and its surrounding areas, where the doves can be seen in forest fragments, agricultural lands, and urban areas.
Caribbean Region: The Eared Dove is also present in the Caribbean region of Colombia, which includes coastal areas along the Caribbean Sea. In this region, the doves can be found in grasslands, agricultural fields, savannas, and urban settings.
Pacific Region: Along the Pacific coast of Colombia, the Eared Dove can be observed in forest edges, plantations, and human-modified landscapes. This region provides suitable habitats for these doves to forage and breed.
Orinoquía Region: The Eared Dove inhabits the Orinoquía region, which encompasses the vast plains of eastern Colombia. In this region, the doves can be seen in grasslands, agricultural areas, and open habitats
Amazon Region: In the Amazon region of Colombia, the Eared Dove is present in forest edges, clearings, riverbanks, and disturbed areas. While primarily a forest species, they can also adapt to human-altered landscapes in this region
Insular Territories: The Eared Dove may also occur in the insular territories of Colombia, such as in the San Andrés and Providencia archipelagoes. These islands provide additional habitats for the species to thrive.
Taxonomy
The Eared Dove (Zenaida auriculata)
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves (Birds)
- Order: Columbiformes
- Family: Columbidae
- Genus: Zenaida
- Species: Zenaida auriculata
Vocalization
The Eared Dove (Zenaida auriculata)
- Call: The most common vocalization of the Eared Dove is a series of mournful and soft cooing sounds that are often repeated in a rhythmic pattern. This call is pleasant and melodious, consisting of a soft "cooo" or "coo roo coo" that can be heard throughout the day.
- Song: During the breeding season and in territorial interactions, Eared Doves may produce a more elaborate song compared to their typical calls. The song of the male Eared Dove is a series of cooing notes and trills that can be delivered in a rhythmic and repetitive manner to attract a mate or deter rival males.
- Flight Call: When in flight, Eared Doves may emit a distinctive whistling sound produced by the movement of their wings. This flight call is a high-pitched "whirrr" or "whistle" that is characteristic of the species when they take off or fly overhead.
- Contact Calls: Eared Doves also use contact calls to communicate with other doves in their flock or to maintain contact with their mate or offspring. These contact calls can vary in intensity and pitch, helping individuals stay connected and alert to each other's presence.