Straight-billed Hermit
The Straight-billed Hermit (Phaethornis bourcieri) Read in Spanish
Appearance: The Straight-billed Hermit is named for its straight and short bill compared to other hermit hummingbirds. It has a green plumage with a darker green back and a white postocular stripe. The underparts are buffy or cinnamon-colored. This species also has a long, slightly forked tail.
Habitat: Straight-billed Hermits inhabit a variety of forested habitats, including primary and secondary forests, forest edges, and clearings in humid lowland and foothill areas. They are often found near streams, rivers, and other water sources where flowering plants are abundant.
Behavior: These hummingbirds are known for their solitary and territorial behavior. They feed on nectar from flowers, using their specialized bills to extract the nectar. Straight-billed Hermits will also consume small insects for additional nutrients.
Breeding: During the breeding season, males perform courtship displays to attract females. The female constructs a cup-shaped nest using plant fibers, which is often positioned near the edge of a branch or a vertical surface. She lays and incubates two eggs.
Conservation Status: The Straight-billed Hermit is of Least Concern.
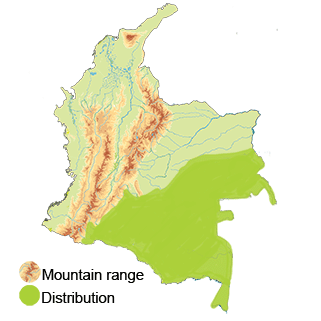
Distribution
The Straight-billed Hermit (Phaethornis bourcieri)
Amazon Basin: In southern Colombia, portions of the Amazon Basin extend into the country, providing additional habitat for the Straight-billed Hermit. The humid and diverse forests of the Amazon region offer rich nectar sources and nesting sites for this species.
Taxonomy
The Straight-billed Hermit ( Phaethornis bourcieri)
- Kingdom: Animalia
- Phylum: Chordata
- Class: Aves (Birds)
- Order: Caprimulgiformes
- Family: Trochilidae
- Genus: Phaethornis
- Species: Phaethornis bourcieri
Vocalization
The Straight-billed Hermit (Phaethornis bourcieri)
- Song: The male Straight-billed Hermit uses its vocalizations, often characterized by a rapid series of high-pitched notes or trills, as part of its courtship and territorial displays. These songs can be a combination of buzzing and chirping sounds that are distinctive to this species.
- Calls: In addition to its song, the Straight-billed Hermit also produces various calls for communication purposes. These calls may include short, sharp notes or rapid chirps that are used to signal alarm, aggression, or to communicate with other individuals within its territory.
- Territorial Displays: Vocalizations are important for establishing and defending territories. The Straight-billed Hermit may use vocal cues to warn off intruders or to attract potential mates during the breeding season.
- Communication: Beyond territorial and courtship purposes, vocalizations also play a role in general communication among Straight-billed Hermit individuals. These birds may use a range of vocal signals to interact with each other within their habitat.